The Embryonic Stem Cell Targeting Process in Mice
Embryonic stem cell or ESC-based gene targeting uses a stem cell’s plasticity to engineer gene targeted mice. Mouse stem cells are first electroporated with a targeting vector. Following successful homologous recombination between the targeting vector and ESC cell DNA, targeted embryonic stem cells are then injected into a normal mouse blastocyst. When injected, the stem cells colonize the blastocyst, resulting in a chimera with cells of distinct genotypes. Blastocysts are then implanted into a host mouse that will carry and deliver it. Finally, chimeric (founder) mice are bred with strains of mice to produce animals that have germline transmission of the targeted gene.
Advantages of Biocytogen’s ESC-based gene editing
Although traditional way to edit genomes but ESC/HR based gene editing offers following advantages:
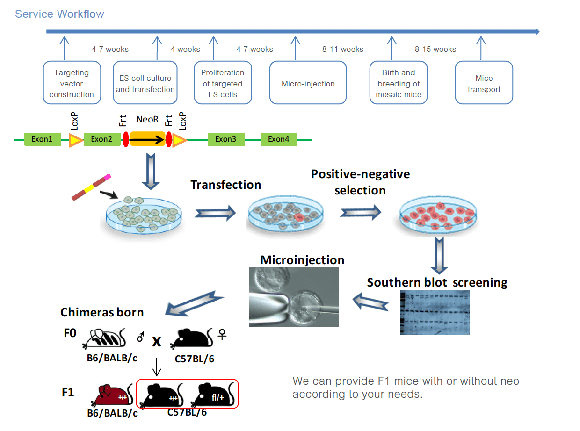
Service Workflow

Knockout Mouse Models
In ESC-based gene knockout targeting, we use a positive selection marker to replace an exon of a targeted gene. The targeted gene is deleted globally, whereas in conditional knockout animals the gene is deleted only in selected cells, as determined by a tissue specific promoter. Conditional knockout mouse models are usually generated using Cre-LoxP or Flp-Frt recombination systems.
Knockin Mouse Models
To generate a knockin mouse, a DNA fragment of interest is inserted at the desired location in the genome. This modality also allows for a variety of models to be created including point mutant, reporter (GFP), tagged (FLAG), Cre, and humanized mice.

Request a Quote
Contact us today to find out how we can help advance your research with custom generated rat, mouse or cell line models.
Publications
Microglial P2Y12 Receptor Regulates Ventral Hippocampal CA1 Neuronal Excitability and Innate Fear in Mice
Peng J, Liu Y, Umpierre AD, et al. Microglial P2Y12 receptor regulates ventral hippocampal CA1 neuronal excitability and innate fear in mice. Mol Brain. 2019;12(1):71. Published 2019 Aug 19. doi:10.1186/s13041-019-0492-x
NRP-1 interacts with GIPC1 and α6/β4-integrins to increase YAP1/∆Np63α-dependent epidermal cancer stem cell survival
Oncogene 37, 4711-4722 (2018).